On-grid Solar Systems (A Comprehensive Guide)
Exploring the realm of renewable energy, on-grid solar setups have become a favored choice among homeowners. These setups, also called grid-tied systems, connect to the local utility grid, ensuring a smooth power supply that adapts to your changing energy demands. In contrast to off-grid systems, which operate independently, on-grid systems let you treat the grid like a storage space, saving surplus energy for later use.
Meanwhile, hybrid systems bring together the strengths of both on-grid and off-grid setups, providing the dependability of on-grid systems combined with the self-sufficiency of off-grid ones. Each system boasts its unique advantages and suits different situations. However, for many, the blend of cost-effectiveness and reliability renders on-grid solar setups an appealing choice.
| Key Points | Details |
| Relevance of 35 kW Solar Systems in Pakistan | These systems combat electricity price fluctuations and promote sustainability. They cost between PKR 7.5–9 million. |
| Types of 35 kW Solar Systems | There are three types: On-Grid, Off-Grid, and Hybrid, each with unique functionalities, benefits, and drawbacks. |
| Cost Factors for 35 kW Solar Systems | The cost varies based on the brand of solar panels and inverters, the type of system, and installation charges. The price range is PKR 4,251,000 to PKR 4,322,000. |
| Return on Investment (ROI) | The ROI is favorable due to potential savings on electricity bills and a payback period of three to six years. Government/utility company subsidies can significantly impact the system’s payback period. |
| Benefits for Businesses and Large Residences | Key benefits include reduced power costs, energy independence, decreased carbon emissions, and the potential to elevate business operations. |
| Importance of 35 kW Solar Systems | These systems are important in Pakistan’s energy landscape. More businesses and residences are encouraged to invest in solar energy systems for economic and environmental benefits. |
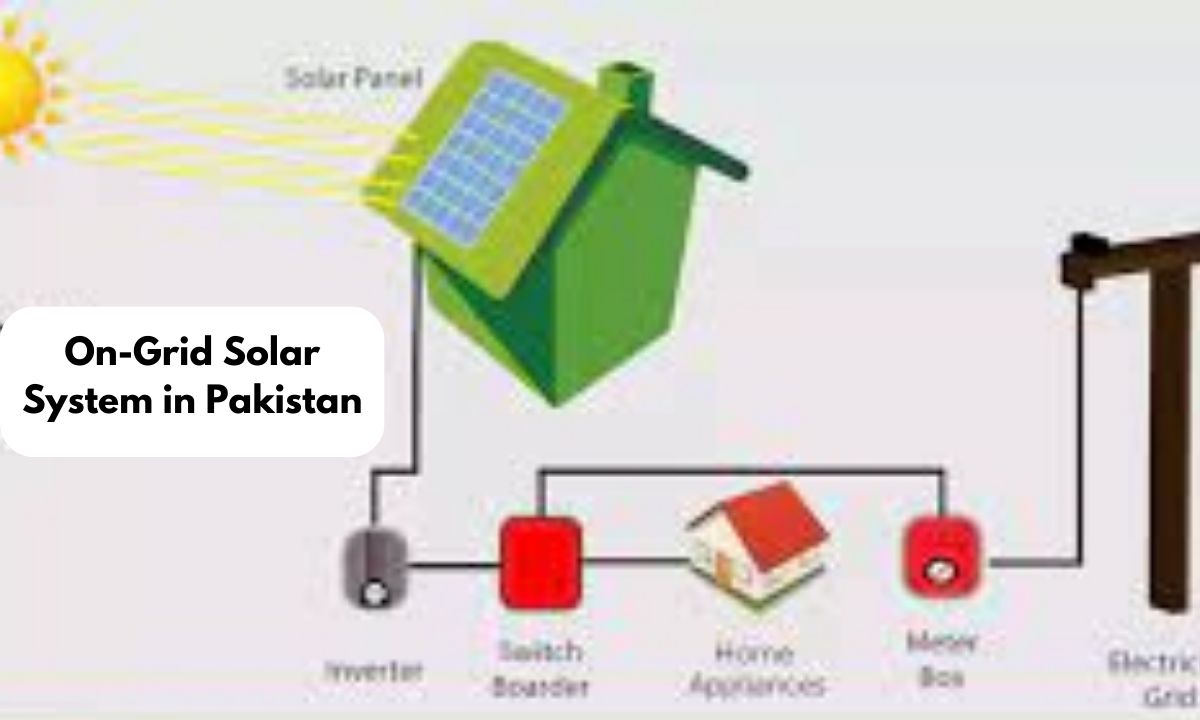
Components of On-grid Solar Systems
In the world of solar power, on-grid solar systems, also called grid-tied systems, are made up of different important parts that team up to turn sunlight into electricity and send it into the electrical grid. Let’s break down each part:
PV Racking System Think of this as the solar panel’s support system, whether it’s on a roof or the ground. It has things like flashings, mounts, rails, and clamps to make sure the solar panels stay securely in place and angled to grab the most sunlight.
Combiner Box This box acts like a meeting point, bringing together the power from multiple solar panels into one line that goes to the inverter. Inside, you’ll find PV string fuses, DC molded case circuit breakers, and DC surge protection devices to keep the system safe and easy to monitor.
Charge Controller This controller keeps an eye on the voltage and current going to the batteries and stops them from getting overcharged. Some controllers even have cool features like low voltage disconnect (LVD), lighting controls, and adjustable settings for different battery types.
Inverter The inverter is a big deal. It changes the DC current from the solar panels into AC current, the kind the electrical grid uses. It has a converter circuit, a capacitor, and a power inverter circuit. Inverters are also important for smart grids, which try to make electricity use more efficient.
Electricity Grid This is the power network that gives electricity to everyone. In on-grid solar systems, the grid is like a backup that can also take in extra electricity the solar panels make.
Safety Switches These switches, like disconnect switches, keep the system safe. They let you isolate parts of the solar system for maintenance or emergencies.
Cabling Cables link up all the parts of the solar system. They need to be the right size and rating to carry the electricity safely and efficiently.
Each of these parts does a big job of making sure an on-grid solar system works well. They make sure solar power turns into electricity, goes to the grid, and keeps everything safe and lasting a long time.
Working of On-grid Solar Systems
Converting Sunlight into Electricity
In the realm of on-grid solar systems, also called grid-tied systems, the magic happens when sunlight transforms into electricity. It’s a bit like a dance, starting when sunlight kisses the solar panels. These panels are like special workers with photovoltaic (PV) cells made of stuff like silicon. When sunlight, made of tiny bits called photons, meets these PV cells, it gets soaked up, and its energy races to the electrons in the silicon.
Now, picture this: the energy jolts those electrons into action, setting them free to zoom around. This buzzing movement creates something called direct current (DC) electricity. But hold on, most homes and the electrical grid speak another language called alternating current (AC). So, we need a hero – the solar inverter. This gadget transforms DC electricity into AC electricity, the kind that powers our homes and buildings.
Routing Electricity to the Grid
Once the electricity is all dressed up in AC, it’s ready for a journey into the electrical grid. This connection happens through a clever system called net metering or something similar. When your on-grid solar setup makes more electricity than your place needs, the extra power takes a ride onto the grid. It’s like sharing a delicious cake – spreading the surplus where it’s wanted.
This whole process follows a rulebook from the past, the Public Utility Regulatory Policy Act of 1978 (PURPA). It tells power providers to buy this extra electricity, usually handled by net metering. Here’s the cool part: your electricity meter keeps tabs on how much you use from the grid and how much you send back. You earn credits for the extra electricity, like a reward that helps pay for the times you need power from the grid.
Now, picture the power grid like a busy city. It’s a network of power wizards – generators, substations, transformers, and power lines – all connected. This network knows how to shuffle electricity around, making sure everyone gets what they need. When your on-grid solar system shares its electricity, it becomes part of this big team, boosting the overall power supply and making the most of renewable energy. It’s like being a green superhero in the world of electricity.
Installation Process of On-grid Solar Systems
- Prepare Your Equipment: Begin by gathering all the necessary materials for your solar setup. This includes solar panels, an inverter, wiring, and mounting hardware. It’s crucial to choose materials that work well together and match the size of your system.
- Install the Mount: Choose a sunny spot and install the mount – whether it’s on the roof or the ground – to get the most sunlight exposure.
- Position the Solar Panels: Place the solar panels on the mount and secure them tightly to withstand strong winds and storms.
- Set Up the Wiring: Connect the panels with wiring. Most modern solar panels come with user-friendly locking connectors to make installation safe and straightforward.
- Attach the Solar Inverter: Link the solar inverter to the system. This gadget does the important job of turning the DC electricity from the panels into the AC electricity we use at home.
- Connect the Solar Inverter to the Power Grid: Now, connect the solar inverter to the power grid. This lets the electricity produced by your solar system flow into the grid.
- Switch on the Solar Inverter: Finally, flip the switch on the solar inverter, and voila! Your system is up and running, producing clean electricity.
Advantages of On-grid Solar Systems
- Cutting Down on Electricity Costs: On-grid solar setups can make a big dent in your electricity bills. Homeowners may slash their energy expenses by a substantial 62% with solar panels. The actual savings depend on factors like system size, sunlight exposure, and the cost of electricity from the grid.
- Low-Maintenance Advantage Without Batteries: One neat perk of on-grid solar setups is that they don’t need batteries. This means no extra costs or hassle in maintaining them. It keeps the whole system simple and budget-friendly.
- Earning Money on the Side with Extra Electricity: On-grid solar setups can even bring in some extra cash by selling surplus electricity back to the grid. Thanks to net metering, solar energy system owners get credits for the electricity they contribute to the grid.
- Syncing Up with Other Power Sources: On-grid solar setups can team up with other power sources, like a diesel generator. This comes in handy when grid power isn’t available.
- Smart Investment Returns: When it comes to return on investment (ROI), on-grid solar systems outshine other types. Their lower cost, minimal upkeep, and reduced monthly power bills make for a solid ROI, reaching as high as 25%. That means for every Rs. 1,00,000 invested in solar, the customer can pocket Rs. 25,000.
- Flexibility for the Future: On-grid systems are great because you can easily expand them to match your changing energy needs.
- Using Electricity Wisely: These systems encourage efficient electricity use, which is not just good for your wallet but also for the environment.
- Grid as a Virtual Battery: The power grid plays a cool role as a virtual battery for on-grid solar systems. It stores extra power without needing much maintenance or replacements, and it does so with impressive efficiency.
On-Grid Solar System Price in Pakistan
Determining the cost of on-grid solar systems in Pakistan hinges on the system’s capacity and the components bundled with it. Here’s a breakdown of prices for various capacities based on the latest available data:
- 3kW On-Grid Solar System: Priced between PKR 500,000 to PKR 700,000.
- 5kW On-Grid Solar System: Approximately PKR 850,000 to PKR 1,000,000.
- 6kW On-Grid Solar System: Ranging from PKR 750,000 to PKR 1,100,000.
- 10kW On-Grid Solar System: Varies from PKR 1,350,000 to PKR 1,650,000.
- 20kW On-Grid Solar System: Though prices for this capacity aren’t explicitly mentioned, a 30kW system costs around PKR 40-45 lacs, providing an estimated range for the 20kW system.
It’s crucial to bear in mind that these prices can shift based on factors like brand, quality, warranty, and additional features such as net metering. The overall costs generally cover solar panels, inverters, mounting structures, wiring, taxes, and installation. However, keep in mind that net-metering charges are not part of these prices. For the most precise and current pricing, it’s advisable to obtain quotes from multiple suppliers, factoring in the specific requirements of your installation.
Cost-effectiveness of On-grid Solar Systems
Advantages of On-Grid Solar Systems: A Wise Investment in Power
Introduction: On-grid solar systems, often called grid-tied solar setups, offer a smart and economical way to generate electricity. These systems connect directly to the national electricity grid, giving homeowners the power to produce their electricity and sell any extra energy back to the grid.
Cost Comparison Between On-Grid and Off-Grid Systems: Comparing the costs of on-grid and off-grid systems reveals that on-grid solar setups are generally more budget-friendly to install and maintain. For example, as of 2023, a 10kW on-grid solar system in Pakistan costs between PKR 1,600,000 to 1,800,000, while a 10kW off-grid system ranges from PKR 2,100,000 to 2,300,000. The higher cost of off-grid systems is mainly due to the need for a larger battery bank to meet overall energy needs.
Monthly Electricity Bill Reduction: On-grid solar systems bring a noticeable reduction in monthly electricity bills. The savings depend on factors such as the system’s size, the sunlight a property receives, and the cost of grid electricity. On average, homeowners can enjoy savings ranging from 50% to 80% on their monthly electricity bills with the right solar system.
Profit Potential Through Net Metering: Beyond reducing electricity bills, on-grid solar systems can be a source of profit through net metering. This system enables homeowners to sell any extra electricity generated by their solar panels back to the grid. In some cases, individuals can accumulate over 50,000 rupees in credit, which can be used to offset their summer bills.
Return on Investment (ROI): The payback period for on-grid solar systems in Pakistan typically spans from 5 to 7 years. This implies that the initial investment in the solar system can be recovered through savings on electricity bills and potential profits from surplus electricity within this period. After the payback period, the electricity generated by the solar system essentially becomes free, leading to substantial long-term savings.
In conclusion, investing in on-grid solar systems not only contributes to a sustainable future but also proves to be a wise financial decision, offering both immediate and lasting benefits.
Conclusion
Embracing on-grid solar systems emerges as a smart and environmentally friendly choice for powering our homes. These systems not only trim down our electricity bills but also actively contribute to preserving the environment by tapping into renewable energy sources.
The simplicity of on-grid systems, sans the need for batteries, makes maintenance hassle-free, and keeps long-term costs in check. Additionally, the chance to earn extra income through net metering serves as a financial perk for homeowners.
What’s more, on-grid solar systems smoothly sync up with existing power sources, ensuring a steady flow of electricity. The promising return on investment further sweetens the deal, leading to substantial savings on energy expenses over time.
Considering these compelling advantages, it becomes advantageous for individuals and communities to ponder over the adoption of on-grid solar systems. In doing so, they actively participate in a global push towards cleaner energy, enjoy financial benefits, and contribute to steering us towards a more sustainable future.





